ARCHIVES (2017)
Do roku 2016 raport oznaczony numerem 1 był tworzony za okres od 1 kwietnia do 31 maja. Od roku 2017 analizy są wykonywane o dekadę wcześniej czyli 1 raport oznacza okres od 21 marca do 20 maja
Communication report regarding the incidences of drought conditions in Poland
Year: 2017; period: 09 (11.VI - 10.VIII)
The Institute of Soil Science and Plant Cultivation – State Research Institute, in accordance with an Act of the Minister of Agriculture and Rural Development has developed the climatic water balance for all 2478 Polish local districts and, on the basis of soil categories, calculated the current risk of agricultural drought for the following crops: winter and spring cereals, grain maize and maize for silage, potatoes, sugar beet, hops, tobacco, ground vegetables, fruit shrubs and trees, strawberries and legumes.
In the ninth reporting period, i.e. from June 11th to August 10th 2017, IUNG-PIB stated n° agricultural drought conditions in Poland.
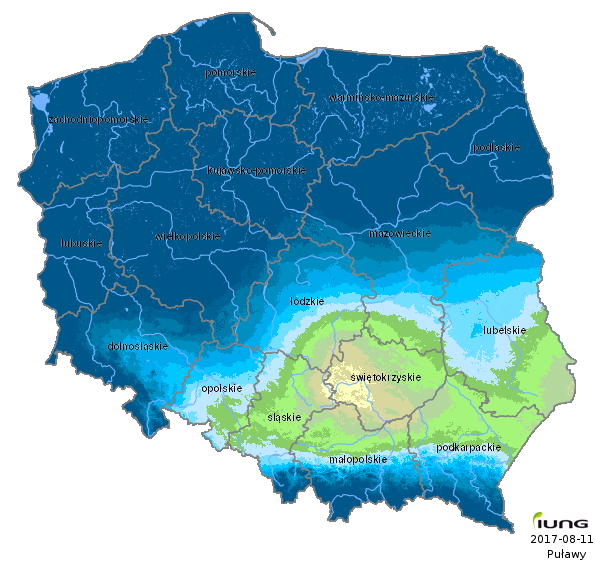
The average value of Climatic Water Balance in Poland in the current sixty-day reporting period has increased in relation to the previous one by 1mm and reached -44 mm. The Climatic Water Balance map has not changed significantly during the last 10 days, only in the north of the Lubelska Upland water deficiency slightly decreased, by 10 mm. In the whole country CWB values were higher than -170 mm and did not exceed the critical values for any of the monitored crops.
The lowest CWB values, from -150 to -169 mm were still recorded in the Małopolska Upland.
June was characterised by highly diversified temperatures. The lowest temperatures were recorded in the vast majority of northern Poland, from below 14 to 16°C. However, they remained within the multiannual norm. The highest temperatures were recorded in the southern and western parts of the country, ranging from 18 to more than 19°C and exceeding the multiannual norm by 2-2.5°C. In the vast majority of the country the temperatures in June exceeded the multiannual norm by 1-2°C.
The first two decades of July were cold, but the third one was warmer. The lowest temperatures were recorded in the north-eastern regions of Poland, ranging from below 15 to 16°C in the first and second decade, and from 17 to 19°C in the third. Considerably higher temperatures occurred in the south-western and southern regions, ranging from 17 to more than 18.5°C in the first and second decade, and from 19 to more than 20.5°C in the third.
The first decade of August was warm. The lowest temperatures occurred in the north of Poland, ranging from 19 to 20°C. Much higher temperatures were recorded in central Poland, from 19 to more than 22°C, and the highest in the south, ranging from 22 to more than 23°C.
June was highly diversified in terms of precipitation distribution. In the southern and south-eastern parts of the country it was very scarce and ranged from below 20 to 50 mm. It constituted 50-70% of the multiannual norm. More intense precipitation occurred in the north-western and north-eastern parts of Poland, ranging from 100 to 160 mm and constituting from 150 to more than 230% of the norm. In the majority of the country precipitation ranged from 50 to 100 mm and exceeded the multiannual norm even by 50%.
In the first decade of July relatively intense precipitation occurred in three areas: in the north, south and central part of the country, where it ranged from 20 to 80 mm. In the rest of Poland precipitation was scarce, from 5 to 20 mm or, at times, below 5 mm. In the second decade of the month, in the north-eastern and western regions precipitation remained relatively intense (20-80 mm), while in the lubelskie region precipitation was very intense and ranged from 80 to more than 100 mm. Low precipitation, below 10 mm was recorded in the south-eastern part of Poland. In the vast majority of the country it ranged from 5 to 30 mm. In the third decade of July intense precipitation occurred in the north-western and northern regions, ranging from 40 to more than 100 mm. Only in the Małopolska and Lubelska Uplands and in the southern Masovia it ranged from 5 to 20 mm.
In the first decade of August precipitation was less intense. However, in the region of Greater Poland and Lubusz Land it was still quite abundant, ranging from 30 to 80 mm. Very low precipitation was recorded in the north-western part of the country, and in the Silesian, Małopolska and Lubelska Uplands, where it did not exceed 10 mm, or at times even 5 mm. In the rest of the country precipitation ranged from 10 to 30 mm.
Water deficiency slightly decreased in the previously affected areas. In the northern part of the Lubelska Upland the CWB values were lower by about 10 mm in comparison to the previous reporting period.
Report prepared by:
Mgr Tomasz Jóźwicki
Dr hab. Rafał Pudełko
Dr Katarzyna Żyłowska
Mgr Piotr Koza
Mgr Elżbieta Wróblewska
Reports
- Report 14 (1.VIII - 30.IX)
- Report 13 (21.VII - 20.IX)
- Report 12 (11.VII - 10.IX)
- Report 11 (1.VII - 31.VIII) +
- Report 10 (21.VI - 20.VIII)
- Report 09 (11.VI - 10.VIII)
- Report 08 (1.VI - 31.VII)
- Report 07 (21.V - 20.VII)
- Report 06 (11.V - 10.VII) +
- Report 05 (1.V - 30.VI) +
- Report 04 (21.IV - 20.VI)
- Report 03 (11.IV - 10.VI)
- Report 02 (1.IV - 31.V)
- Report 01 (21.III - 20.V)