ARCHIVES (2014)
Do roku 2016 raport oznaczony numerem 1 był tworzony za okres od 1 kwietnia do 31 maja. Od roku 2017 analizy są wykonywane o dekadę wcześniej czyli 1 raport oznacza okres od 21 marca do 20 maja
Communication report regarding the incidences of drought conditions in Poland
Year: 2014; period: 05 (11.V - 10.VII)
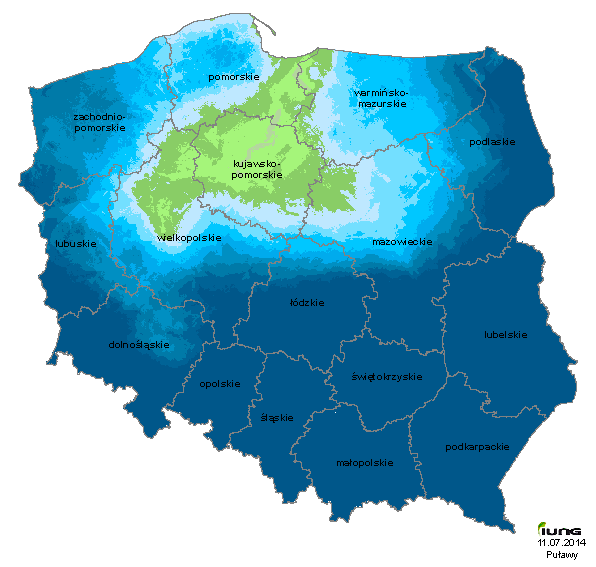
In the fifth reporting period, i.e. from May 11 to July 10, 2014, IUNG-PIB does not state a risk of agricultural drought in Poland. The values of climatic water balance (CWB), which are the basis to assess the risk of drought in most areas, are negative, but these values for the above-mentioned crops are much higher than the critical value.
The lowest CWB values in the current reporting period, occurred in the same area as in the previous reporting period, except that these values were about 20-30 mm below previous. In the Grudziądzka and the Kwidzyńska Valley the CWB ranged from -140 to -149 mm. Low values also were recorded in the Central Noteć Valley, Chełmiński Lakeland, Świecka Upland, in the Torun Valley from -130 to -139 mm. In addition, the low value of CWB continues to occur in Ilawa, Chodzież, Żuławy lake districts, at Tuchola Lowlands, and in those areas were from -120 to -139 mm.
The highest values of CWB, amounting to approximately 100 mm was recorded in Głubczyce Plateau. High values were also in the Lublin Upland and Woźnicko-Wielunska Upland where ranged from 50 to 80 mm.
For the whole country the average value of the CWB in the current reporting period was lower than the previous period by 15 mm.
May this year, in terms of thermal conditions was relatively diverse. The highest air temperature occurred in eastern and south- eastern part of Poland, reaching more than 14°C. In most parts of the country temperature of 13 to 14 oC were recorded. The coldest was in the north of the country and in the mountains, in these regions the air temperature was 11-12oC. In most parts of the country, the air temperature in May was within the long term norm, only higher than the long-term average by 1o C was recorded in the north of the country.
In the first ten days of June highest air temperature occurred in western Poland, reaching in Ziemia Lubuska and the Śląska Upland highest temperature ranging from 17.5 to 18.5oC. In the large area of Poland, temperature ranged from 16.5 to 17.5oC. In the eastern part of north country, the temperature was lower and ranged from 15.5 to 16.5oC.
The second ten days of June was relatively cold. The warmest areas of the country was the western and south-western parts of Poland with temperatures ranging from 16 to 18oC and the coldest areas of the north-eastern parts of Poland with temperature from 13 to 16oC.
Definitely the third ten days of June was the coldest. In north-eastern parts of Poland air temperature was even below 13.5°C. In most parts of Poland temperature ranged from 13.5 to 15oC, only in the north of Podkarpacie was a little warmer and ranged from 15.5 to 16oC.
The first ten days of July was relatively warm. The warmest area was in the northern part of the country, from 20 to 21.5 °C, but without the Podlasie Lowland and eastern parts of the Mazury Lake District, where the air temperature in these areas ranged from 19 to 20oC. In the south of the country the temperature was lower, less than 19oC, and definitely the coldest was in Podhale and the Bieszczady Mountains amounting around 17.5oC.
In May precipitation was very diverse. The lowest precipitation occurred in the north and especially in the north-eastern part of the country from 20 to 100 mm, and accounted for 100% of long-term norm. The farther south, the rainfall values were higher, and were exceeding long-term norm by over 100%. The highest rainfall from 100 to over 300 mm was recorded in the Sudety, Lublin Upland, eastern and western Beskidy, Podhale and Tatry. The long-term norm were exceeded in the western parts of Poland like Malopolska Upland, Podhale, Tatry (over 250%), and in the Lublin region by as much as 350%. In some places, record precipitation was not noted even for decades.
Precipitation in the first ten days of June was very varied, from small, few millimeter in Ziemia Lubuska, Śląska Upland and the Karpaty Foothills and western Beskidy, to 5 to 20 mm occurring over a large area of the country. In the east part of the north parts of the country, precipitation was higher, ranged from 20 to 40 mm and at the edge of the country rainfall amounted to 50 mm.
In the second ten days of June the highest rainfall was recorded in the northern part of the country ranging from 30 to 60 mm, the further south the rainfall was lower and in the Polish Uplands were even less than 5 mm. In southern Poland precipitation was little larger, from 5 to 20 mm.
The third ten days period of June was characterised with large variation in terms of precipitation. The relatively low values of rainfall were recorded in Wielkopolskie Lakeland of around 10 mm. In large areas of the north-western Poland rainfall ranged from 10 to 25 mm. In contrast, high precipitation were recorded in the south-eastern part of the country ranging from 50 to 100 mm, and in some places of the area amounted to more than 150 mm.
The first decade of July was characterized by great diversity in terms of precipitation. Very large precipitation occurred in the Izerskie Foothills, in the Western Carpathians, Śląskio-Krakowska and Lublin Upland, as well as in Oleśnicka Plain, in these regions recorded rainfall ranged from 50 to over 100 mm. On the large Polish area precipitation ranged from 10 to 50 mm, while the smallest rainfall was recorded in north-eastern part of the country, amounting to less than 10 mm.
Reports
- Report 13 (1.VIII - 30.IX)
- Report 12 (21.VII - 20.IX)
- Report 11 (11.VII - 10.IX) +
- Report 10 (1.VII - 31.VIII) +
- Report 09 (21.VI - 20.VIII) +
- Report 08 (11.VI - 10.VIII)
- Report 07 (1.VI - 31.VII)
- Report 06 (21.V - 20.VII)
- Report 05 (11.V - 10.VII)
- Report 04 (1.V - 30.VI)
- Report 03 (21.IV - 20.VI)
- Report 02 (11.IV - 10.VI)
- Report 01 (1.IV - 31.V)